Interventional diagnostics
The principal methods of interventional oncology are as follows:
1.Tumor chemoembolization
This method consists in the introduction of embolizing agents saturated or mixed with a chemical drug into the arteries supplying blood to the tumor. The most commonly performed procedure is chemoembolization of the hepatic artery. The method is one of the basic ones in the treatment of hepatocellular cancer and metastases of hypervascular tumors. It enables to achieve a significant tumor necrosis, to increase the patient life span.
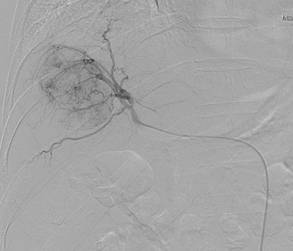
Hepatocellular cancer of the right liver lobe. Angiography prior to chemoembolization.
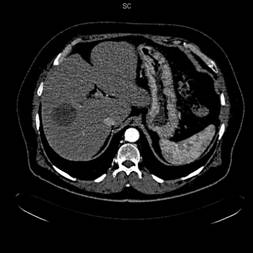
Computed tomography 6 months after chemoembolization. Complete tumor necrosis.
2. Tumor embolization
This method consists in the introduction of embolizing agents such as particles of hemostatic sponge, polyvinylalcohol; microspheres, embolizing glue and polymer substances, metal spirals. Embolization is mainly used with the preoperative aim to reduce blood loss in the course of the subsequent surgical intervention and for arrest of bleeding caused by tumor or as a result of surgical intervention. Embolizations of actually all sites are performed: renal arteries, uterine arteries, arteries supplying blood to bone and soft tissues, head and neck tumors.
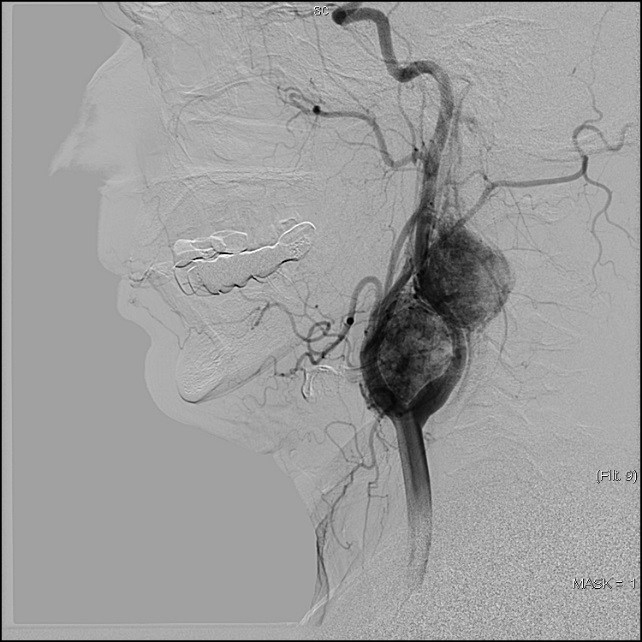
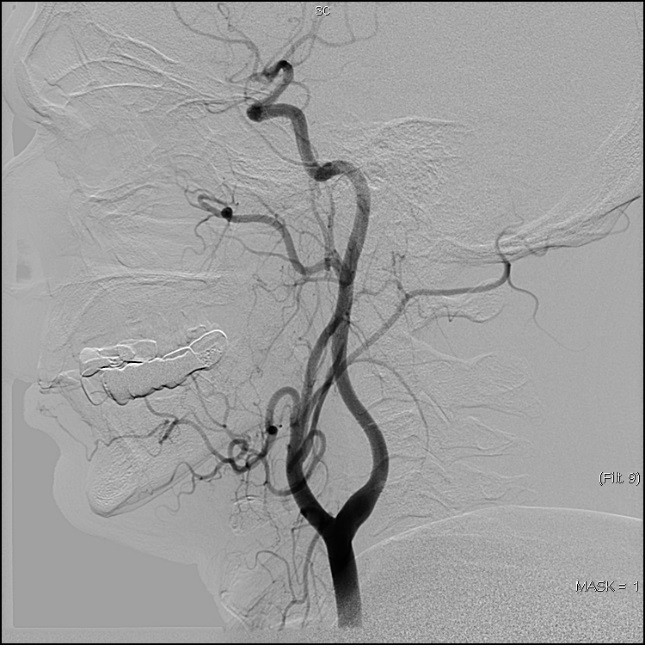
Angiograms before and after embolization in a patient with multiple neck paragangliomas
Tumor of the right kidney prior to ablation and one year after it. Complete tumor necrosis.
Before
After
3.Radiofrequency tumor ablation
This method consists in thermic exposure by applying alternating electric current via the electrode introduced into the tumor.With tumor sizes up to 3 cm, the ablation efficacy is comparable with the results of surgical treatment. Ultrasound-guided (without incision) percutaneous ablations are performed; the specialists also participate in performing radiofrequency ablations in the course of extended surgical hepatic interventions. The main ablation applications are hepatic and renal tumors.
Tumor of the right kidney prior to ablation and one year after it. Complete tumor necrosis.
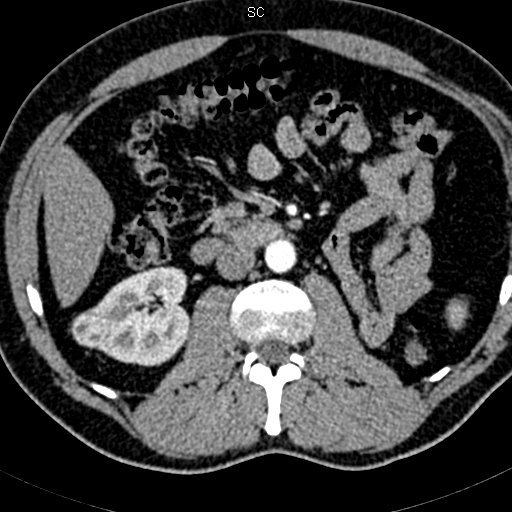
Before
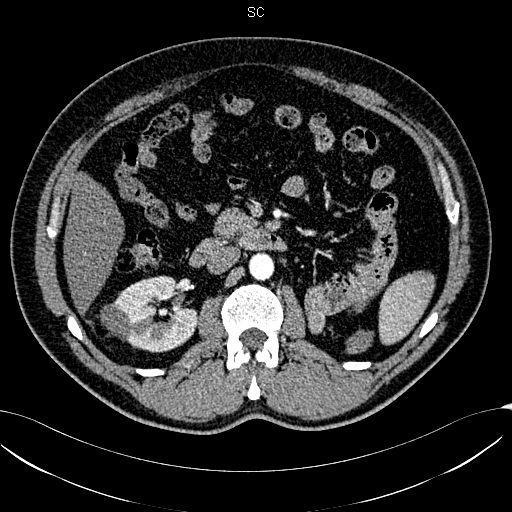
After
4. Stenting and draining of biliary ducts
Percutaneous draining and stenting of biliary ducts are performed for the obstructive jaundice syndrome of tumor genesis. With this abnormality caused by pancreas head tumors, biliary duct tumors, hepatic tumors, these procedures are the only real cure for the patients in most of the cases. Our specialists have gained broad experience in performing the interventions (more than 1500) being routine procedures.
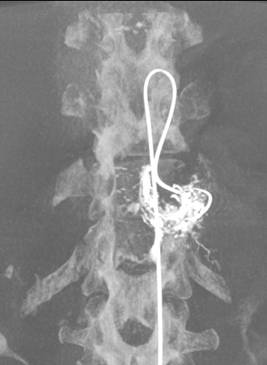
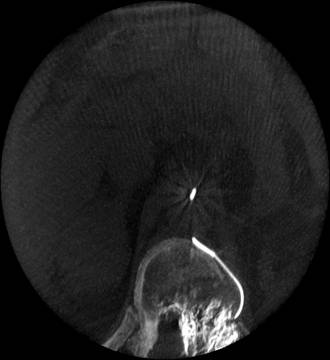
Pancreatic cancer with common biliary duct obstruction.
Unobstructive entrance of bile to duodenum after stenting.
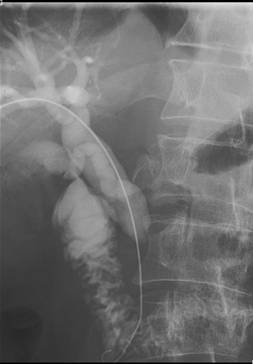
Before
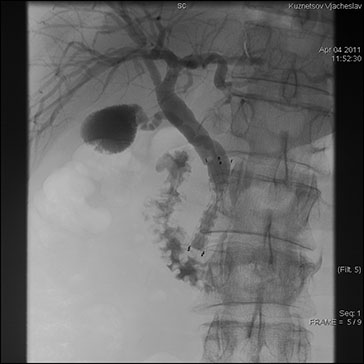
After
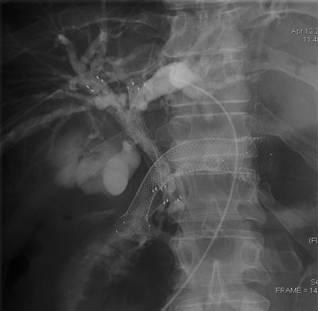
5.Stenting of esophagus, trachea, large intestine, pylorus and duodenu
Malignant obstructions of hollow organs originate with far-advanced tumors and cause the syndromes of dysphagia, intestinal obstruction, respiratory failure. Stenting enables to restore the organ lumen without surgical intervention, thus considerably improving the patient life quality.
Biliary stenting and pyloroduodenal stenting in a patient with obstructive jaundice and pyloric tumor.
6.Endovascular treatment of arteriovenous malformations
Our specialists have acquired experience in the treatment of peripheral arteriovenous malformations by employing embolization with spirals, microspheres, ethanol. Embolization makes it possible to achieve clinical effect (hemorrhage arrest) and cosmetic effect. Most of the patients have been suffering from arteriovenous malformations for decades, their surgical treatment being inefficient and unrealizable. An adequate endovascular treatment requires repeat procedures.
7. Angiography
All angiography techniques are applied being carried out on the two-projection angiography apparatus “Innova Electric Medical System”. The most demandable angiography techniques are carotid angiography, angiography of lower extremities, coronarography. Great experience has been gained in performing selective and superselective angiographies being of vital importance in oncology. 3D angiographies are performed for head and neck abnormalities with possible reconstruction of images similar to computed tomography images.
3D angiography of metastasis in the thoracic vertebra with obtaining CT-like scans
Before
After
8.Other interventions
The Angiography Room also performs drainages of abscesses and fluid masses in abdominal organs, nephrostomies, cava filter implantations. The specialists operating in the Room are in close contact with clinicians, the decisions about the most optimal treatment modality for a patient are made jointly.












