Magnetic resonance imaging
To early detect and efficiently treat the diseases of various organs and systems, definitive diagnosis is needed. The most effective modality for obtaining information is magnetic resonance imaging.
What is it – magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)?
MRI is an investigation modality based on the utilization of magnetic and radiowaves and also of a computer transducing the image.
The operating MRI-scanner generates a magnetic field setting the protons of hydrogen atoms into a radiowave beam.
Layer-by-layer imaging of MRI structures allows to diagnose a lesion at its initial stage in a short space of time.
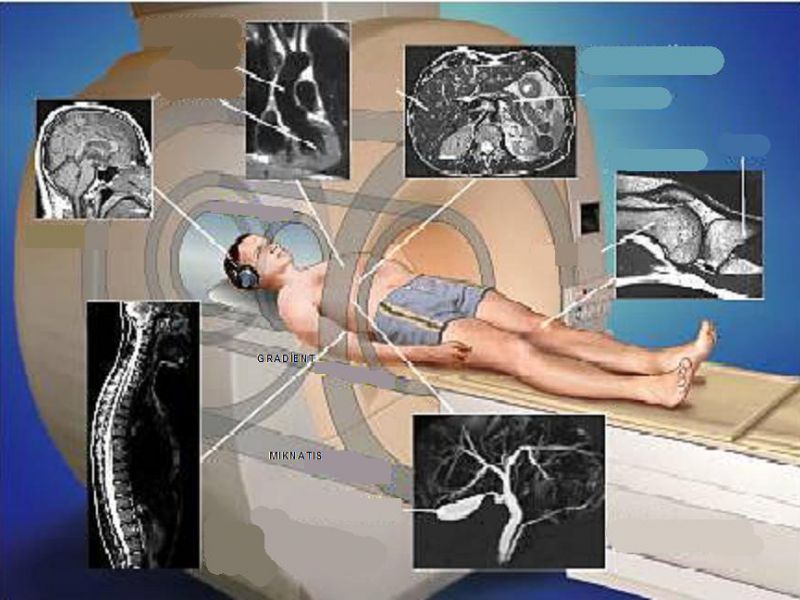
Reasons for the study
Organs or systems being subject for this modality:
- Brain tomography
- Testing of brain vessels (arterial and venous angiograms)
- Spinal marrow and spine (lumbosacral, pectoral, cervical parts)
- Vessels of the neck
- Brain tomography with narcosis (or spinal marrow)
- Testing of adrenals
- All major joints
- Abdominal cavity
- Small pelvis organs
In addition to diagnosing disorders of internal organs or diseases (testing of any body part is possible ¬ from brain to toes), checkup of the therapeutic or surgical effect may be a reason for study.
How to get ready for MRI
Making a choice of a diagnostic centre in Minsk, you should pay attention not only to the span of time you’ll have to wait for your turn but also to tomographic scanner performance. In case of sedatives being prescribed, the way home is to be thought over.
Food and water intake is ceased for 4 hours before the procedure. Sedatives (if prescribed) are taken 1-2 hours before (if not otherwise prescribed by the doctor).
Before the procedure, the patient in clinic is inquired about:
- Medicosurgical history
- Renal condition (when introducing contrast-enhancing medium with paramagnetic characteristics)
- Presence of pregnancy and allergy
- Presence of objects in the body which may affect the results of the study: heart pacemaker, hearing aid, neurostimulator, metal crumbs in eyes or other body parts, insulin pump, metal plates, pins, screws, aneurysm clamps, unextracted bullet.
As a rule, brackets or dental fillings do not cause problems, whereas jewelry, spectacles, hearing aids and metal products should be taken off, as well as plasters with drugs containing metal capable of causing a burn.
It is advisable to put on ear plugs or ear-phones (the sound produced by the tomographic scanner is quite loud). To make the diagnosis more accurate, contrast-enhancing medium may be intravenously introduced, if indicated by the doctor. The prescribed drugs should be taken as scheduled.
The procedure lasts 30-60 min.
MRI limitations
- age under 7 years
- weight: up to 180 kg
- waist height: up to 32 cm
- waist volume: up to 140 cm
What’s to be done after testing
After termination of MRI procedure you need to wait for the results of image studying. Additional testing may be necessary. Having analysed the images, the radiologist forwards them to the attending doctor and tells the patient about the results and subsequent stages of testing and treatment.
If the patient was taking sedatives, he/she ought not operate machinery, drive a car or make any major decisions until the effect of the drug is over.
If the contrast-enhancing medium was taken in the lactation period, the doctor should specify the time of breast feeding resumption. No side effects of gadolinium used in tomography are observed in children.
Procedure-related complications
On the occasion of patient’s condition aggravation, allergy or uncommon symptoms (pain, post-injection edema) after tomography, be sure to consult the attending doctor.












